Conventional
Food that is not certified organic is called “conventional” or “commercial,” meaning that it or its ingredients may be sprayed with pesticides, grown with synthetic fertilizers, and contain genetically modified organisms. Some producers may follow organic practices without having their products certified as organic because of the cost or complexity of certification.
Cooperative
A co-op is a business owned, operated, and democratically-controlled by its owners to meet their common needs and aspirations. Cooperatives operate according to seven basic principles. There are various kinds of cooperatives: consumer, producer, and worker, to name a few. Willy Street Co-op is a consumer cooperative, where its customers can join if they like.
Fair Trade
There are several different agencies that certify products as “Fair Trade.” Each of these uses their own unique standards, but the most widely used system across the globe, considered by many to be the gold standard, is the Fair Trade International system. This certification has four main components:
- Minimum Price. Fair Trade International publishes a minimum price that must be paid to any farmer for Fair Trade products. This price varies by country, and acts as a safety net to ensure that producers are paid enough to cover their cost of production and living expenses.
- Environmental Standards. The rigorous environmental sustainability component to the Fair Trade International certification includes mandating that farmers preserve and nurture their soils and natural ecosystems; that they reduce their use of greenhouse gases; and that they refrain from using certain toxic chemicals.
- Working Conditions. This includes a prohibition on child labor and forced labor, an emphasis on gender equality, the rights of workers to associate, paid time off, and occupational health and safety requirements such as adequate toilet facilities, access to clean drinking water, and protective gear for staff doing hazardous work.
- Fair Trade Premium. In addition to the minimum price requirement, each sale of a Fair Trade product generates a Fair Trade premium, which is money entrusted to farmers and farmworkers with the stipulation that it must be spent on farm infrastructure or the welfare of workers, their families, or their community.
Local
At Willy Street Co-op, "local" means the product was sourced from anywhere in Wisconsin or from within 150 miles of the state capitol building (see image below).
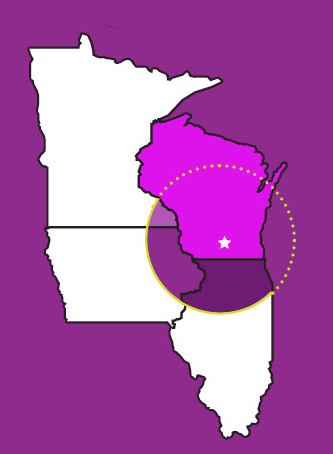
Local products are noted with purple signage at our Co-op.
Natural
The term "natural" has no regulatory definition, but when referring to food it usually means having no artificial preservatives or colors and minimal ingredients.
Organic
The USDA organic regulations describe organic agriculture as the application of a set of cultural, biological, and mechanical practices that support the cycling of on-farm resources, promote ecological balance, and conserve biodiversity. These include maintaining or enhancing soil and water quality; conserving wetlands, woodlands, and wildlife; and avoiding use of synthetic fertilizers, sewage sludge, irradiation, and genetic engineering.
Organic producers use natural processes and materials when developing farming systems—these contribute to soil, crop and livestock nutrition, pest and weed management, attainment of production goals, and conservation of biological diversity.
Wild-Crafted
The term refers to uncultivated herbs, plants, or fungi gathered from the wild. Because they are harvested from the wild, they cannot be certified organic, however farms can get a portion of their wooded acreage certified as organic.